
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a rare but serious condition characterized by an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain. This vascular anomaly disrupts normal blood flow and oxygen delivery, posing significant health risks if left untreated. This blog explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebral AVM to spread awareness and provide valuable insights.
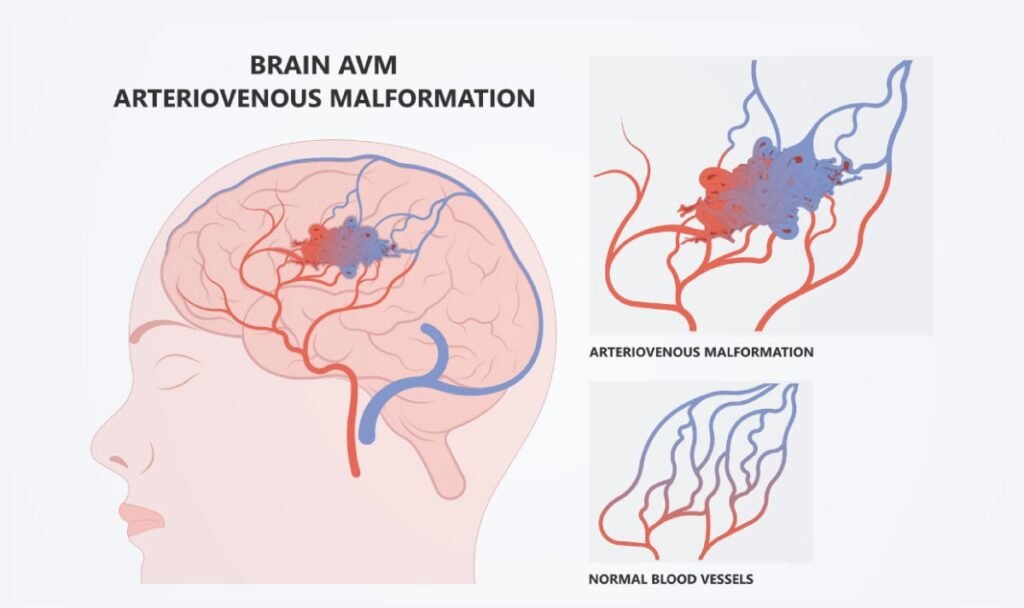
What is Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
A cerebral AVM is a congenital disorder in which arteries and veins in the brain are interconnected without the normal capillary network. This bypass leads to high-pressure blood flow, increasing the risk of vessel rupture and subsequent bleeding in the brain. While AVMs are present at birth, symptoms typically manifest later in life, often between ages 10 and 40.
Common Symptoms of Cerebral AVM
Many individuals with cerebral AVM remain asymptomatic for years, but others may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
Severe Headaches: Persistent or sudden headaches that may worsen over time.
Seizures: Unprovoked and recurring episodes of abnormal brain activity.
Weakness or Numbness: Often on one side of the body, depending on the AVM’s location.
Vision Problems: Difficulty seeing clearly or experiencing partial vision loss.
Difficulty Speaking: Problems with speech or understanding language.
These symptoms may mimic other neurological conditions, making early diagnosis crucial.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of cerebral AVM remains unknown. However, it is believed to be congenital—present from birth—and may result from abnormal blood vessel development during fetal growth. Although rare, AVMs may also have a genetic component in certain cases.
Age: Symptoms commonly appear between ages 10 and 40.
Risk factors include:
Family History: Rare familial cases suggest a genetic predisposition.
Potential Complications
Cerebral AVMs are associated with severe complications, including:
Brain Hemorrhage: The most critical risk, occurring when an AVM ruptures.
Stroke: Due to reduced oxygen flow or bleeding.
Neurological Damage: Long-term deficits caused by pressure on brain tissue.
Epilepsy: Persistent seizures as a result of AVM activity.
Diagnosing Cerebral AVM
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms indicative of AVM, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention. Diagnosis typically involves:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the brain’s structures.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Detects bleeding in the brain.
Cerebral Angiography: A specialized imaging test to visualize blood vessels and confirm the presence of AVM.
EEG (Electroencephalogram): Used if seizures are a predominant symptom.
Treatment Options
The treatment of cerebral AVM depends on its size, location, and symptoms. Common approaches include:
Medication: To manage symptoms such as seizures or headaches.
Surgery:
Microsurgical Resection: Complete removal of the AVM.
Endovascular Embolization: Minimally invasive procedure to block blood flow to the AVM.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Focused radiation to shrink and eventually close the AVM over time.
Observation: In cases where the AVM is small and asymptomatic, regular monitoring may be recommended.
Living with Cerebral AVM
Coping with a cerebral AVM diagnosis can be challenging. Here are some tips for managing the condition:
Follow Medical Advice: Regular check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments are essential.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoid activities that increase blood pressure, as they may heighten the risk of rupture.
Seek Support: Counseling or support groups can help individuals and families cope emotionally.
Be Aware of Symptoms: Recognizing early warning signs can be life-saving.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help
Seek emergency medical care if you experience:
Sudden, severe headaches.
Weakness, numbness, or paralysis.
Loss of vision or speech difficulties.
Seizures or fainting episodes.
Conclusion
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Awareness of its symptoms and risks can lead to timely medical intervention, improving outcomes significantly. If you or someone you know shows signs of cerebral AVM, consult a healthcare professional without delay.
Stay informed, stay safe.

